Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
2008 July 12
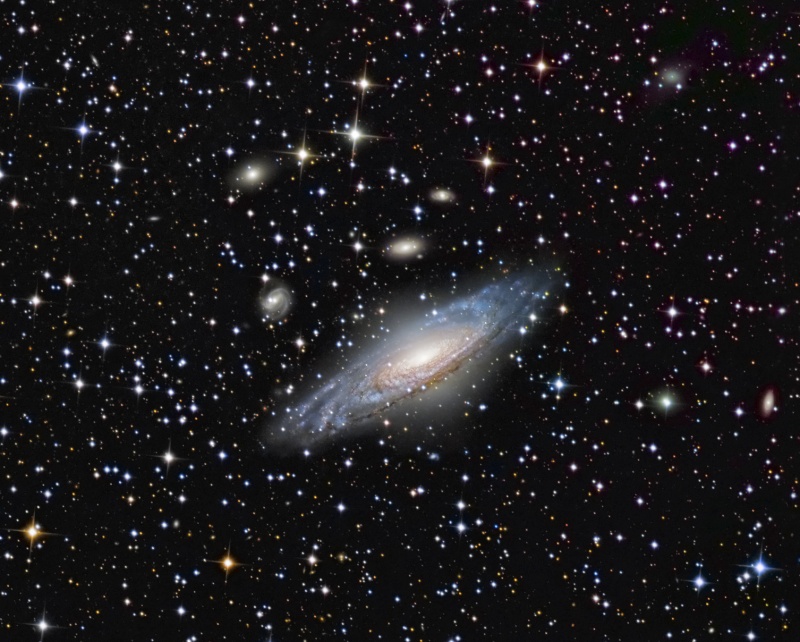

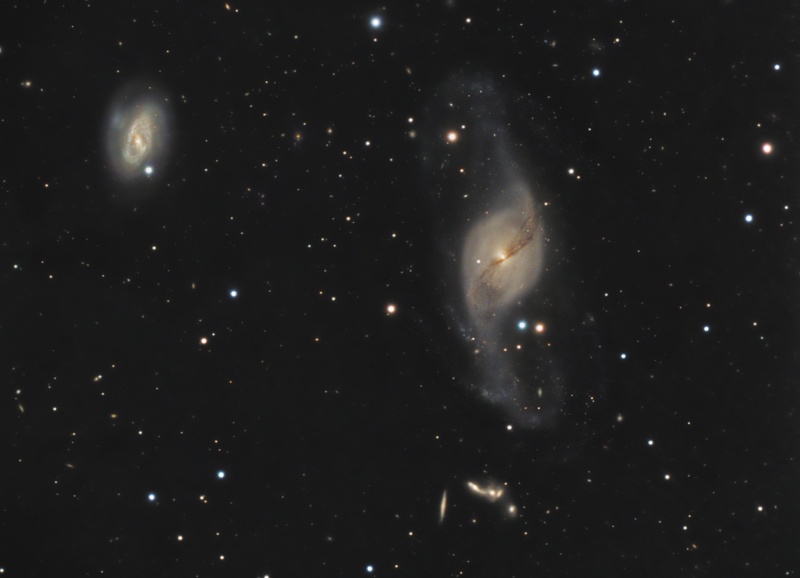
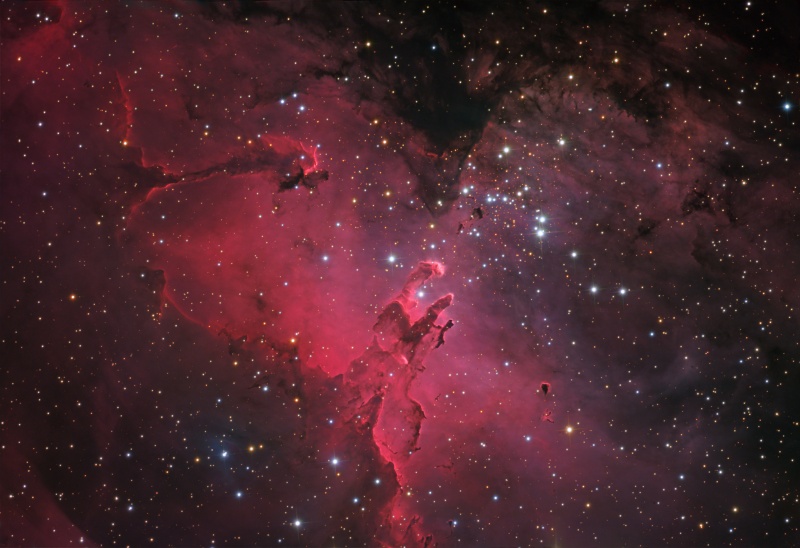
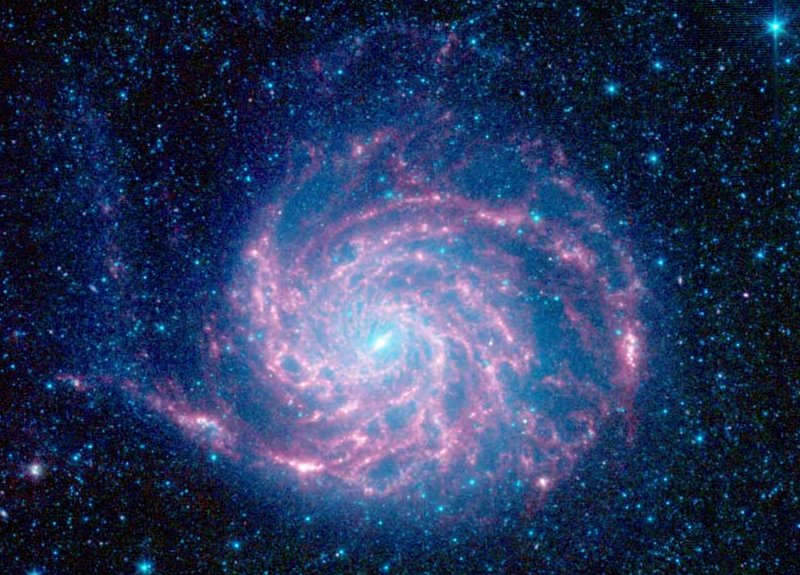
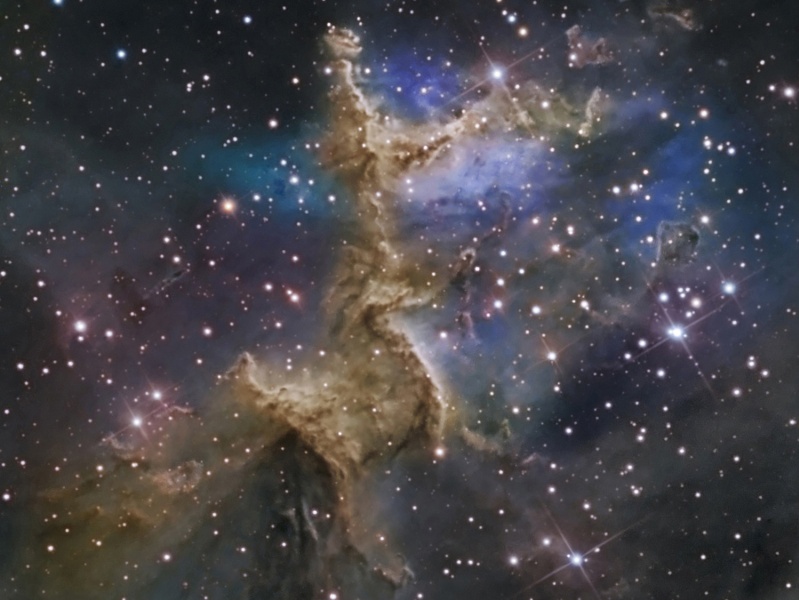
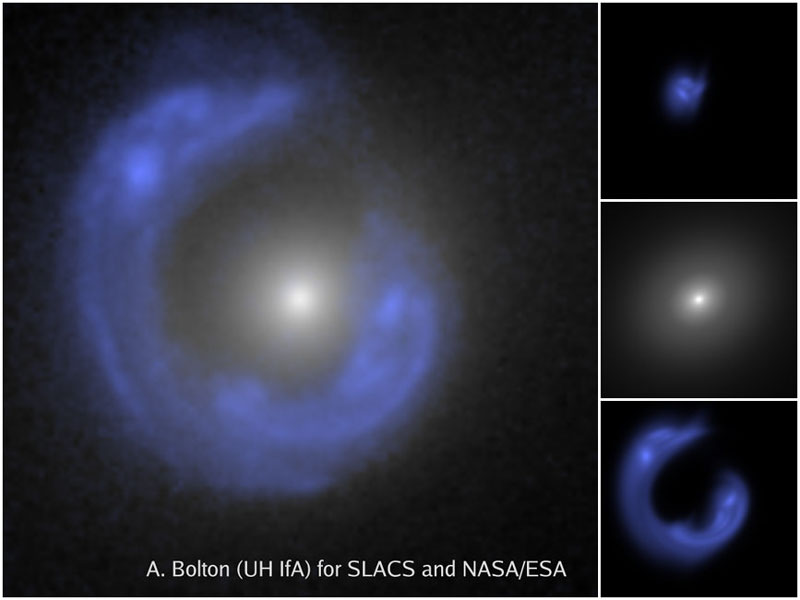
NGC 7331 and Beyond
Credit & Copyright: Don Goldman, Sierra Remote Observatories Explanation: Big, beautiful spiral galaxy NGC 7331 is often touted as an analog to our own Milky Way. About 50 million light-years distant in the northern constellation Pegasus, NGC 7331 was recognized early on as a spiral nebula and is actually one of the brighter galaxies not included in Charles Messier's famous 18th century catalog. Since the galaxy's disk is inclined to our line-of-sight, long telescopic exposures often result in an image that evokes a strong sense of depth. The effect is further enhanced in this well-framed view by the galaxies that lie beyond this gorgeous island universe. The background galaxies are about one tenth the apparent size of NGC 7331 and so lie roughly ten times farther away. Their strikingly close alignment on the sky with NGC 7331 occurs just by chance. The visual grouping of galaxies is also known as the Deer Lick Group.
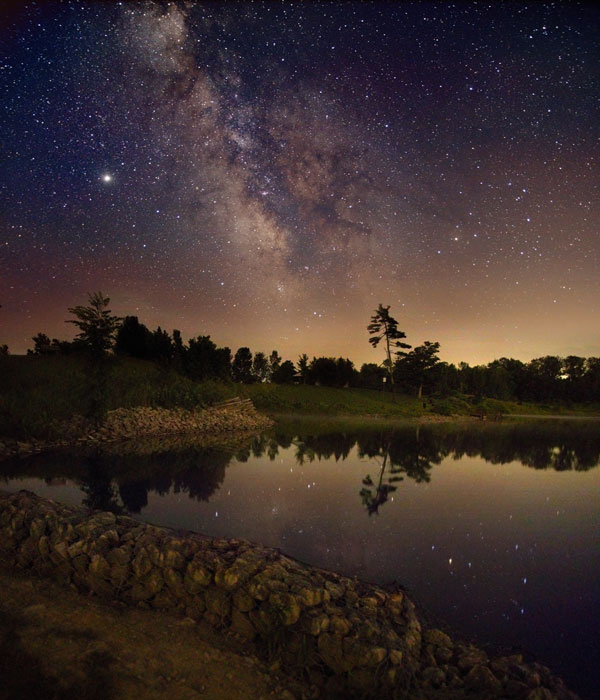
Tomorrow's picture: valley and sky
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
2008 July 12

NGC 7331 and Beyond
Credit & Copyright: Don Goldman, Sierra Remote Observatories Explanation: Big, beautiful spiral galaxy NGC 7331 is often touted as an analog to our own Milky Way. About 50 million light-years distant in the northern constellation Pegasus, NGC 7331 was recognized early on as a spiral nebula and is actually one of the brighter galaxies not included in Charles Messier's famous 18th century catalog. Since the galaxy's disk is inclined to our line-of-sight, long telescopic exposures often result in an image that evokes a strong sense of depth. The effect is further enhanced in this well-framed view by the galaxies that lie beyond this gorgeous island universe. The background galaxies are about one tenth the apparent size of NGC 7331 and so lie roughly ten times farther away. Their strikingly close alignment on the sky with NGC 7331 occurs just by chance. The visual grouping of galaxies is also known as the Deer Lick Group.
Tomorrow's picture: valley and sky